Multi-cloud Atlas deployments are a special case of multi-region deployment in which you set up cluster nodes across multiple geographic regions and multiple cloud providers. Multi-cloud deployments enhance protection in the case of concurrent regional outage and cloud provider outage. By automatically rerouting traffic to a different cloud provider's node in another region, you get continuous availability and a smooth user experience. Multi-cloud deployments can also protect against vendor lock-in and enhance performance.
Atlas supports multi-cloud deployment across any combination of AWS, Azure, and GCP.
To learn how to configure multi-cloud deployments and learn about the different types of nodes you can add, see Configure High Availability and Workload Isolation in the Atlas documentation.
Use Cases for Multi-Cloud Deployments
The following image shows a multi-region, multi-cloud Atlas deployment for regions that support availability zones. Note that this differs from a multi-region deployment only in that multiple cloud providers are used.
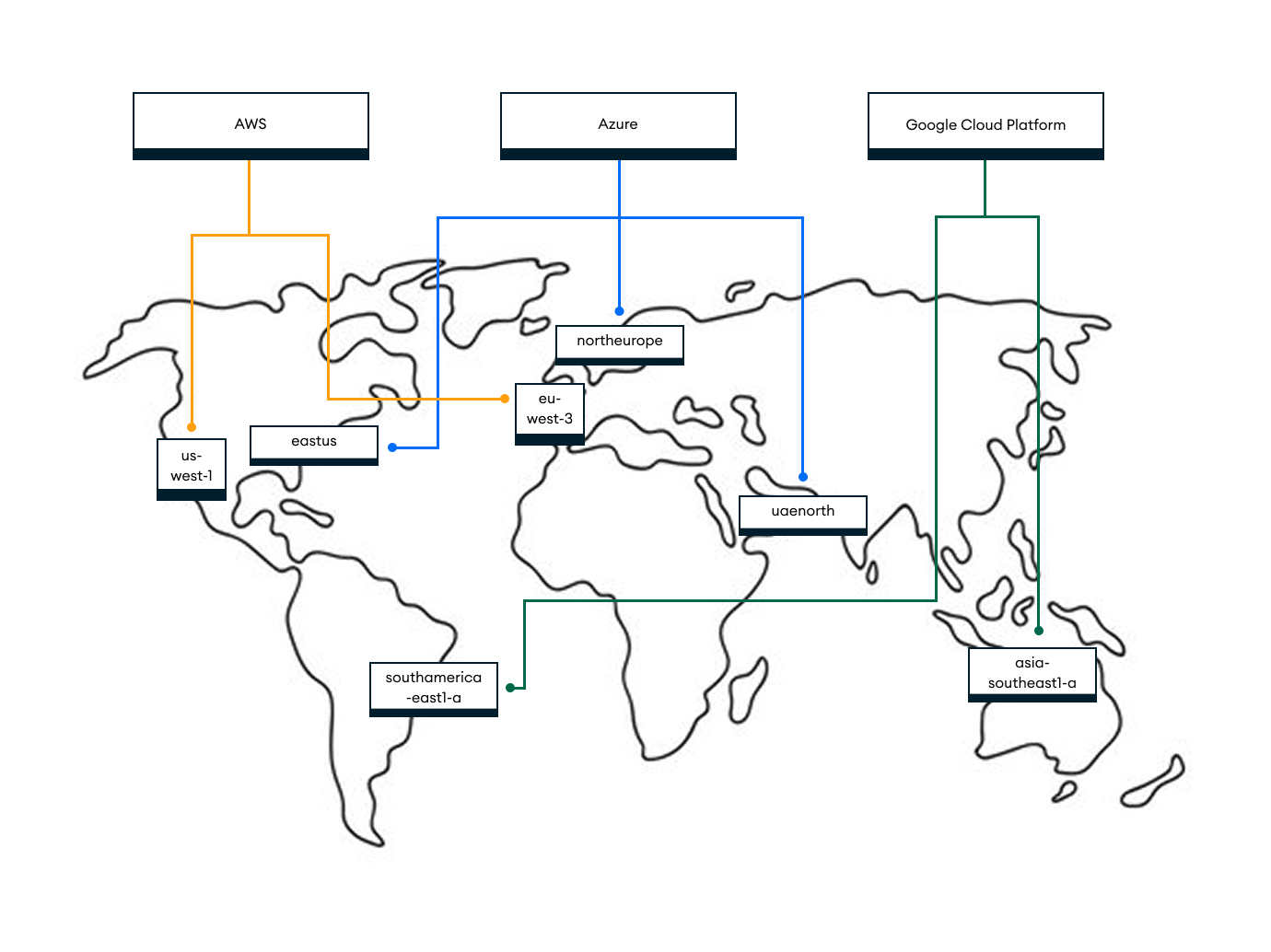
A multi-region, multi-cloud deployment may be best for you if you want to:
Provide an application development team with the option to use any one of the cloud providers for deploying their application stack (including the Atlas cluster).
Migrate an application to a new cloud provider. You can add a node to a new cloud provider region, and Atlas will replicate the data to that new node.
Ensure faster data recovery if there is a cloud provider failure. If the backup is replicated to a separate cloud, automation will bring up a full app stack on a separate cloud and remount the backup to start serving traffic.
Run analytics on a separate cloud. For example, your the data science team wants to use BigQuery for business intelligence but your app stack is in AWS.
Deploy your application stack on both AWS and Azure and serve read and write traffic from both clouds, whether sharded or not.
Considerations and Recommendations
Multi-cloud deployments have the same considerations and recommendations as other multi-region deployments. In addition, the following are specific considerations for multi-cloud deployments:
Cost. Since you are getting charged higher rates for ingress/egress traffic on both cloud providers during replication.
Complexity of the deployment. There are many integrations you may want when deploying an Atlas database, and many of them are pinned to a single cloud provider. For example,
Encryption key management for KMS integration / encryption at rest.
Secrets management for database access.
Integration with a SSO federated identity provider.
Private networking, because each cloud provider only peers (uses private endpoints) with other regions within that provider.
Gather observability data like logs, metrics, and alerts in a centralized place.
Therefore, multi-cloud deployments often require 3rd party integrations to meet these needs.